Key Takeaways
- Macro trends, driven by economic, technological, political and social factors, shape industries and offer both opportunities and risks for businesses.
- Understanding macro trends allows businesses to adapt proactively, refine strategies and remain competitive in an evolving market.
- By leveraging tools like Porter’s Five Forces and PESTLE analysis, companies can identify key success factors and turn macro trends into actionable strategies for growth and resilience.
The world is interconnected, so macroeconomic trends can ripple through entire industries, shaping how businesses operate and thrive. Whether it’s a shift in tariff policies or changes in consumer spending habits, these overarching movements often have outsized effects on the way companies function and compete.
For businesses aiming to stay ahead, understanding macro trends is no longer optional—it’s essential. These trends influence everything from consumer behavior and technological advances to broader economic forces. However, navigating these shifts effectively requires a solid grasp of industry dynamics and strategic foresight. By understanding macro trends, businesses can adapt proactively, ensuring they stay relevant in an evolving market.
What is a macro trend? And why do they matter?
A macro trend is a large-scale, long-term movement that impacts industries, markets and societies. IBISWorld covers these closely in Quarterly Macroeconomic Updates. These trends often emerge from a combination of economic, technological, political and social factors. Some examples include the widespread adoption of digital wallets and the reshoring of manufacturing operations.

Why do these trends matter? The answer lies in their potential to create opportunities or risks for businesses. Macro trends can disrupt traditional models, spark innovation and influence consumer preferences—all of which directly affect how industries evolve. For professionals in commercial banking, accounting, consulting, academia, marketing and beyond, staying informed about these trends offers a competitive advantage.
- Commercial Banking: Understanding shifts in consumer spending can help tailor products and services. For example, as more people adopt digital wallets and mobile banking, banks that invest in user-friendly apps and secure platforms can maintain a competitive edge. Similarly, credit teams can use the same insights to assess risks more effectively when evaluating borrowers.
- Accounting and Consulting: Macro trends provide a foundation for advising clients on tax changes, market risks and digital transformation. For instance, the rise of remote work has led to new tax considerations and operational challenges that firms must address to support their clients.
- Academia: Research into macro trends helps shape curricula, ensuring students are prepared for future challenges. In preparation for post-graduate life, these trends can direct the future workforce into employment fields of growth potential.
- Private Equity and Investment Banking: Identifying macro trends allows these firms to pinpoint lucrative investment opportunities and form the basis of thematic funds. The growing interest in renewable energy, for instance, has spurred a surge in mergers and acquisitions within the clean energy sector.
- Marketing: Macroeconomic research provides marketers with valuable insights into consumer behavior, spending habits and preferences. By understanding these trends, businesses can craft targeted campaigns that resonate with their audience. For example, during economic downturns, marketers might emphasize value-driven messaging, while periods of growth enable them to focus on premium product offerings. Leveraging macro trend data enables more effective allocation of budgets and the creation of strategies that align with broader market dynamics.
How to identify relevant macro trends and turn them into strategy
Identifying and leveraging macro trends involves a mix of structured analysis and informed decision-making. Tools like Porter’s Five Forces and PESTLE analysis are invaluable in this process.
Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces framework helps businesses assess the competitive forces within their industry and understand how macro trends can shift these dynamics. The five forces—competition intensity, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes and threat of new entrants—allow businesses to predict how external factors like economic shifts or changes in consumer behavior can affect market conditions. By using Porter’s Five Forces to evaluate how macro trends influence competition, businesses can adjust their strategies to stay ahead of competitors, negotiate better supplier deals and improve their market position.

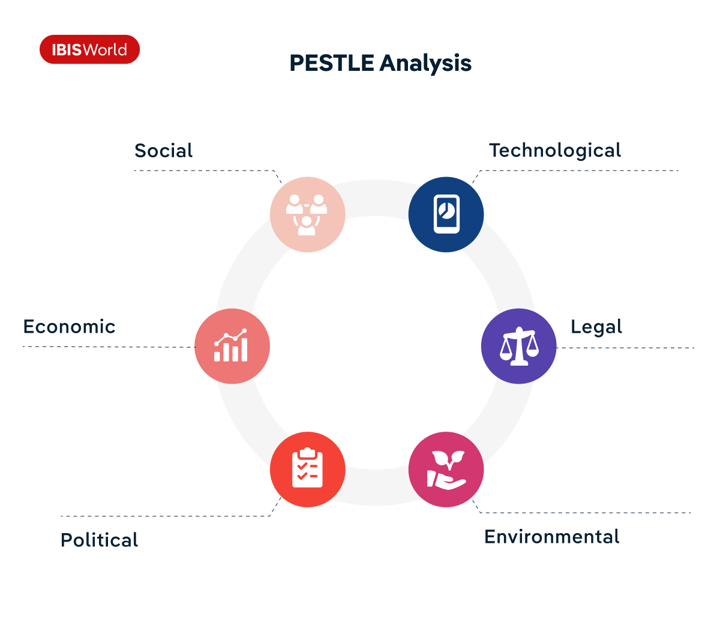
PESTLE analysis
PESTLE analysis offers a structured approach to understanding how macro trends in the political, economic, social, technological, legal and environmental realms impact industries. Each factor in PESTLE can reveal potential risks or opportunities for businesses. For example, shifts in political stability may affect trade policies, while technological advancements can create new business models or disrupt traditional ones. By continuously evaluating these factors, businesses can align their strategies with external macro trends and anticipate changes that could influence their operations, customer behavior or regulatory landscape.
Steps to translate macro trends into strategy
- Monitor Consumer Behavior: Use surveys, market data and trend reports to track shifts in consumer preferences. For example, tracking how younger generations prefer online shopping can help businesses develop new digital strategies.
- Analyze Geographic Variations: Recognize that trends often manifest differently across regions. Tailoring your approach to specific geographic areas can help you meet local demands effectively. For instance, urban consumers may prioritize sustainability more than rural ones, influencing product design and marketing campaigns.
- Forecast Industry Changes: Use macro trends to predict changes in Porter’s Five Forces—such as the intensity of competition or supplier power—to stay agile in responding to market shifts.
- Identify Key Success Factors: Determine what your business needs to succeed in the evolving landscape. This might include investing in new technology, upskilling employees or forming strategic partnerships. For example, companies affected by global tariff changes may prioritize supply chain diversification.
IBISWorld tracks more than 200 Macro Trends. By pairing the steps above with macro trends, businesses can transform abstract ideas into actionable strategies that drive growth and resilience.
Case study: The 2024 US Presidential election
The US presidential election provides a compelling example of how macro trends could influence global industries, particularly through potential shifts in trade policies and tax laws. The second Trump presidency, for instance, might bring about new tariffs and tax reforms, illustrating how political decisions could create global ripple effects across sectors.
If tariffs on steel, aluminum, and Chinese imports were reintroduced or expanded, global supply chains could face significant disruptions. Industries relying on imported raw materials might experience rising costs, prompting businesses to explore alternative suppliers or absorb higher expenses. For example, manufacturers might need to reevaluate cost structures and adjust pricing strategies to maintain profitability. Conversely, domestic producers of goods like steel might temporarily benefit from reduced competition, capturing more market share.

Potential tax reforms under the Trump administration could also underscore the broad impacts of macro trends. Changes to corporate tax rates or deductions might initially increase profitability for some companies while raising concerns about long-term fiscal deficits and potential interest rate hikes.
Industries might adapt in diverse ways. Accounting firms could advise clients on optimizing benefits from revised tax policies while mitigating risks from new compliance requirements. Consulting firms might help businesses navigate supply chain challenges by diversifying operations or considering reshoring production.
These potential macroeconomic shifts wouldn’t be limited to manufacturing and finance. Retailers and marketers might adjust their strategies to focus on cost efficiency and localized production, aligning with consumer expectations for affordable yet high-quality goods. Meanwhile, academics and researchers might analyze these trends to provide insights into broader implications for trade and economic policy.
This speculative case study highlights the importance of macro trend analysis in forecasting challenges and seizing opportunities. By leveraging resources like IBISWorld’s extensive analysis of macro drivers, businesses can make informed decisions, adapt proactively and build resilience in the face of sweeping changes.
Final Word
Macro trends are not just industry buzzwords; they are forces that drive the evolution of markets and shape the future of business. These trends, whether technological, political or cultural, offer invaluable insights into the changing landscape of consumer preferences, supply chains and competitive dynamics.
For businesses, understanding macro trends goes beyond simply reacting to changes. It requires active engagement, strategic adaptation and forward-thinking leadership. Staying informed through reliable resources, conducting rigorous analyses and fostering innovation are essential to maintaining a sustainable competitive advantage.
Adaptability is key. Businesses that proactively respond to macro trends can identify opportunities earlier, mitigate potential risks and position themselves as leaders within their sectors. Whether it’s by embracing new technologies, diversifying supply chains or reshaping customer experiences, the ability to leverage these trends strategically is critical to long-term success.









